Installation and start-up of residential wastewater treatment plant
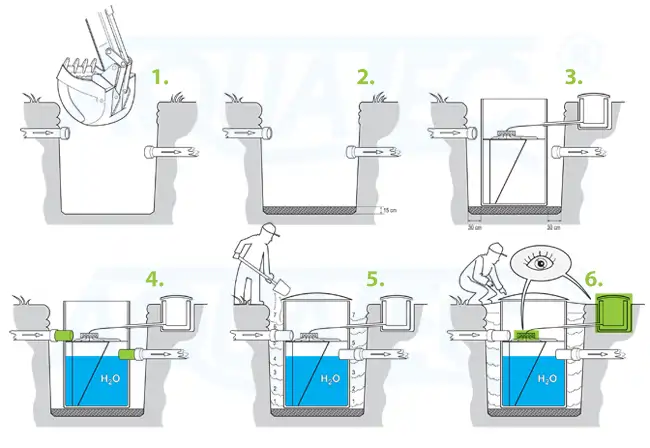
1. Excavating the designated area for AT 6 – AT 20 WWTP:
- Dig a hole
- Build a reinforced-concrete base slab 150 mm thick, flatness +/- 5 mm;
- Create furrows that are directed to the excavation centre for the inlet and outlet piping;
- Lay the pipelines;
- The pipelines should be lead to the excavation in its appropriate length;
- Prepare the inlet piping to be directly connected to the input socket of the wwtp
- The outlet piping in the excavation should end with a socket to allow its connection with the outlet piping from the wwtp;
- Unless the pipelines are led to the hole on the same axis (e.g. due to technical terms), a sufficient number of interconnecting elbow-pipes with the correct angles should be provided on the day of installation
- Decreasing the level of the underground water below the excavation base level;
- Reinspect the flatness of the reinforced-concrete base slab (permitted tolerance +/- 5 mm in all directions). If the flatness is not within the aforementioned tolerance, place the cement layer to achieve the required flatness;
- Make certain there are no objects, stones, clay etc. on the reinforced-concrete base slab;
-
Lay the protective PP or PVC of DN 50 piping below the ground level so the air supply flow from the blower to the wwtp;
(the pipeline serves for the connection hose to pass through which will secure the air blowing from the blower to the wwtp; it should not be more than 5 metres long); - Leading the electric power to the blower location, placing the electric cable into the protective piping according to the applicable Aruba's Technical Norms);
The contractor will perform the preliminary work to the building
2. The installment procedure of the plant:
-
The simplicity of installing the wwtp does not require a professional. But one will be available through the company
Decreasing the level of the underground water below the excavation base level - Reinspect the flatness of the reinforced-concrete base slab (permitted tolerance +/- 5 mm in all directions). If the flatness is not within the aforementioned tolerance CEASE FROM INSTALLING. First place the cement layer to achieve the required flatness;
-
Lay the protective PP or PVC of DN 50 piping below the ground level so the air supply flow from the blower to the wwtp;
(the pipeline serves for the connection hose to pass through which will secure the air blowing from the blower to the wwtp; it should not be more than 5 metres long); - Make certain there are no objects, stones, clay or rainwater inside the plant
- If rainwater is present it must be removed before continuing further procedures;
- The status of the wwtp should be inspected ,so if any damage is revealed, stop the installation of the wastewater treatment plant and contact the supplier. The repairs should be completed before placing the plant in the excavation;
- Make certain there are no objects, stones, clay etc. on the reinforced-concrete base slab;
Stop the installation of the wastewater treatment plant if the slab is not clean.
- Place the wastewater treatment plant on the reinforced-concrete base slab in the excavation;
- By inserting a sewage pipe in the socket of the wastewater treatment plant, make the outlet watertight through the setting of the socket in the sewage pipe on the outlet pipe from the wastewater treatment plant therefore making the sewerage system watertight. If necessary, seal the connection with silicate cement;
- fill the wwtp with water (all segments) to the level of the outlet piping;
- Either fill the perimeter of the plant with the soil or build a concrete encasement in compliance with the building design. When filling with soil, it is necessary to apply 300 mm compacted layers evenly. The soil must be free of stones, building material and other objects, as the plastic tank of the wastewater treatment plant could be damaged.
- The wwtp must be filled with water before filling the perimeter with soil or building the concrete encasement.
The wastewater treatment plant can be installed either by the supplier or the servicing organization. In each scenario, the building work must be performed by the operator unless otherwise agreed upon.
.
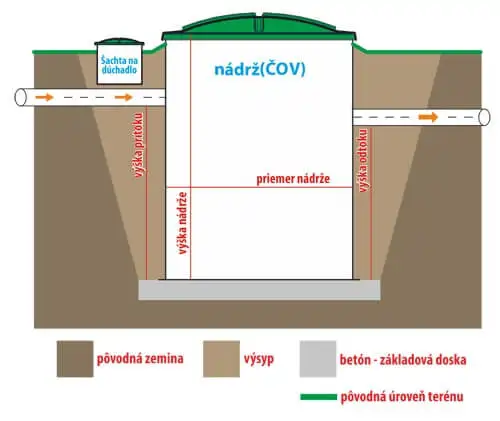
Priemer nádrže - Tank Diameter
Výška nádrže - Tank Height
Výška odtoku - Outflow Height
Výška prítoku - Inflow Height
| TYPE |
Tank diameter [mm] |
Tank height [mm] |
Inflow height [mm] |
Outflow height [mm] |
Manhole diameter [mm] |
DN inflow/outflow [mm] |
| AT 6 | 1400 | 1800 | 1300 | 1150 | 1400* | 125/125 |
| AT 8 | 1400 | 2200 | 1700 | 1500 | 1400* | 125/125 |
| AT 10 | 1750 | 2200 | 1500 | 1250 | 1400 | 125/125 |
| AT 12 | 1750 | 2400 | 1700 | 1500 | 1400 | 125/125 |
| AT 15 | 2050 | 2200 | 1700 | 1500 | 1400 | 150/150 |
| AT 20 | 2050 | 2700 | 2200 | 2000 | 1400 | 150/150 |
* according to selected solution 600 mm.
Installation of the blower shaft
It is advantageous for the customer to purchase the blower shaft for the installation of the blower. The placement of the shaft should be next to the wastewater treatment plant. There is interconnection protective piping with the shaft which simultaneously serves to drain the shaft in the case of irrigation. When placing the blower in the shaft connect it with the air supply hose passing through the interconnecting protective PP-HT DN 50 piping and join at the air timer.
The wastewater treatment plant can be started after the completion of its connection by the consumer, supplier or servicing centre.
3. The wastewater treatment plant start up procedure "by the manufacturer or by customer training from the manufacturer"
The most important step of the wastewater treatment plant is the initial start up therefore it requires the manufacturer or a trained customer from the manufacturer do it.
- fill the wastewater treatment plant with clean tap water to the level of the outlet;
- start the blower;
- check the control valves (see page 6 Operating instructions);
- approximately 200 litres of active sludge should be poured into the inflow part that is taken from the residential wastewater treatment plant or municipal wastewater treatment plant.
